
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Response
- Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected at 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:547-57)
- Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):970-971. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0253
- 2,450 View
- 68 Download
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected At 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists Until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):547-557. Published online March 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0078
- 5,866 View
- 185 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
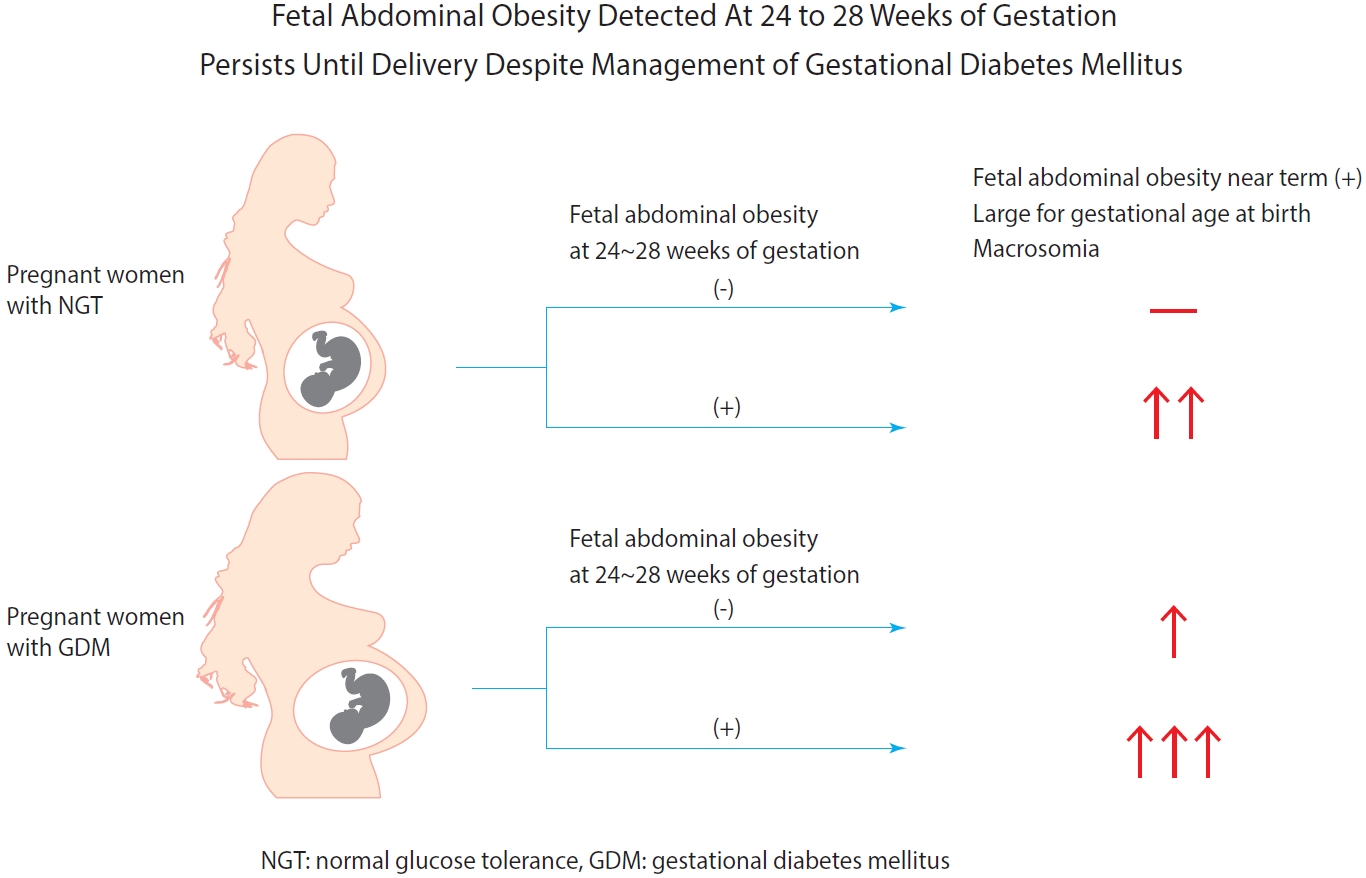
Fetal abdominal obesity (FAO) has been reported to be affected at gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) diagnosis at 24 to 28 weeks of gestation in older and/or obese women. This study investigated whether the management of GDM improves FAO in GDM subjects near term.
Methods
Medical records of 7,099 singleton pregnant women delivering at CHA Gangnam Medical Center were reviewed retrospectively. GDM was diagnosed by 100-g oral glucose tolerance test after 50-g glucose challenge test based on Carpenter–Coustan criteria. GDM subjects were divided into four study groups according to maternal age and obesity. FAO was defined as ≥90th percentile of fetal abdominal overgrowth ratios (FAORs) of the ultrasonographically estimated gestational age (GA) of abdominal circumference per actual GA by the last menstruation period, biparietal diameter, or femur length, respectively.
Results
As compared with normal glucose tolerance (NGT) subjects near term, FAORs and odds ratio for FAO were significantly higher in old and/or obese women with GDM but not in young and nonobese women with GDM. For fetuses of GDM subjects with FAO at the time of GDM diagnosis, the odds ratio for exhibiting FAO near term and being large for GA at birth were 7.87 (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.38 to 14.15) and 10.96 (95% CI, 5.58 to 20.53) compared with fetuses of NGT subjects without FAO at GDM diagnosis.
Conclusion
Despite treatment, FAO detected at the time of GDM diagnosis persisted until delivery. Early diagnosis and treatment might be necessary to prevent near term FAO in high-risk older and/or obese women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of gestational diabetes mellitus on fetal growth: is it different for low-risk and medium–high-risk pregnant women?
Jie Wang, Xin Cheng, Zhen-Hua Li, Yi-Cheng Mao, Xin-Qiang Wang, Kang-Di Zhang, Wen-Jie Yu, Ying-Qing Li, Jia-wen Zhao, Mao-Lin Chen, Guo-peng Gao, Cheng-Yang Hu, Xiu-Jun Zhang
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fetal abdominal obesity and the ensuing adverse perinatal outcomes in older obese pregnant women with or without obesity and with normal glucose tolerance
Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Early-life exposure to gestational diabetes mellitus predisposes offspring to pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Qian-Ren Zhang, Yan Dong, Jian-Gao Fan
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis
Wenrui Ye, Cong Luo, Jing Huang, Chenglong Li, Zhixiong Liu, Fangkun Liu
BMJ.2022; : e067946. CrossRef - Fetal abdominal overgrowth is already present at 20–24 gestational weeks prior to diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus
Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effects of gestational diabetes mellitus on fetal growth: is it different for low-risk and medium–high-risk pregnant women?
- Adiponectin Concentrations in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with or without Metabolic Syndrome.
- Ja Young Park, Ja Won Kim, Ji Min Kim, Ying Han, Soo Kyung Park, Ji Young Mok, Mi Kyoung Park, Hye Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(3):224-235. Published online June 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.3.224
- 2,385 View
- 20 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Adipocytes produce several adipokines that modulate insulin action as well as glucose and lipid metabolism. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between serum adiponectin concentrations and metabolic syndrome (MS) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. METHODS: This study included 127 type 2 diabetic patients (males 63, females 64). The subjects were divided into two groups as with or without metabolic syndrome (MS(+) or MS(-)). The MS was diagnosed by International Diabetes Federation. Serum adiponectin, leptin, fasting plasma insulin, glucose, glycated hemoglobin, lipid profile, white blood corpuscle (WBC), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), uric acid and C-reactive protein (CRP) were examined. RESULTS: Serum adiponectin concentrations were significantly lower in MS(+) than MS(-) (4.8 +/- 2.4 microgram/mL vs 7.6 +/- 5.8 microgram/mL, 7.6 +/- 3.7 microgram/mL vs 11.5 +/- 7.2 microgram/mL, P < 0.05 in males and females). After adjustment for age and body mass index (BMI), in MS (+), the serum levels of adiponectin correlated positively with high density lipoprotein - cholesterol (HDL-C) and negatively with height, body weight, ALT and CRP. In MS(-), the serum levels of adiponectin correlated positively with HDL-C and negatively with diastolic blood pressure (DBP), triglyceride and CRP. By multiple regression analysis, no parameters were independently correlated with serum adiponectin concentrations in MS(+), while DBP and HDL-C were independently related to serum adiponectin concentrations in MS(-). CONCLUSION: Serum adiponectin concentrations were lower in type 2 diabetic patients with MS than without MS. There were no significant parameters related to decrease serum adiponectin concentrations in MS. But further study is needed to confirm this result. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Urinary adiponectin concentration is positively associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications
Won Seon Jeon, Ji Woo Park, Namseok Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Won Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Cheol-Young Park, Byung-Soo Youn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Plasma Osteoprotegerin with Adiponectin and Difference according to Obesity in Men with Metabolic Syndrome
Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(6): 762. CrossRef - The Effects of 12-Weeks Intensive Intervention Program on Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Adipocytokines and Nutrients Intakes in Industrial Male Workers
Kieun Moon, Ill Keun Park, Yeon Sang Jo, Yun Kyun Chang, Yun Mi Paek, Tae In Choi
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2011; 44(4): 292. CrossRef - Relationship between Nutrients Intakes, Dietary Quality, and Serum Concentrations of Inflammatory Markers in Metabolic Syndrome Patients
Misung Kim, Juyoung Kim, Wookyung Bae, Sohye Kim, Yesong Lee, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(1): 51. CrossRef - Prevalence of Pancreatic Cancer in Diabetics and Clinical Characteristics of Diabetes-associated with Pancreatic Cancer - Comparison between Diabetes with and without Pancreatic Cancer -
Seung Goun Hong, Jae Seon Kim, Sung Joo Jung, Moon Kyung Joo, Beom Jae Lee, Jong Eun Yeon, Jong-Jae Park, Kwan Soo Byun, Young-Tae Bak
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2009; 54(3): 167. CrossRef
- Urinary adiponectin concentration is positively associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





